Dual Innervation Of Organs By The Autonomic Nervous System Refers To The Observation That
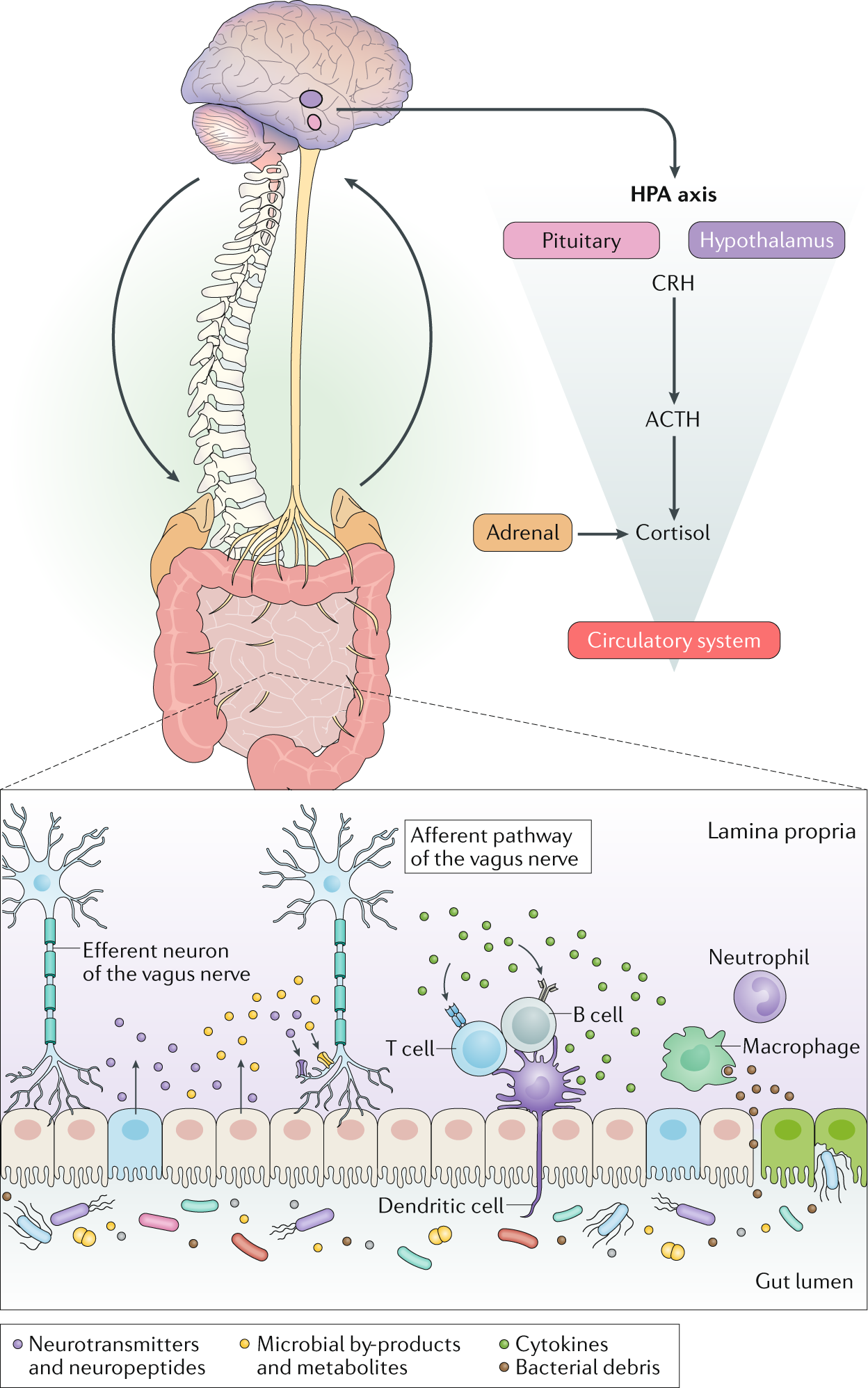
Dual innervation of organs by the autonomic nervous system refers to the observation that. Alterations of the pace and the force of contraction of heart muscles are influenced by the effect of the vagus nerve on the pacemaker cells of the heart. Human Physiology 9th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 7 Problem 2UC. The polyvagal theory describes an autonomic nervous system that is influenced by the central nervous system sensitive to afferent influences characterized by an adaptive reactivity dependent on the phylogeny of the neural circuits and interactive with source nuclei in the brainstem regulating the striated muscles of the face and head.
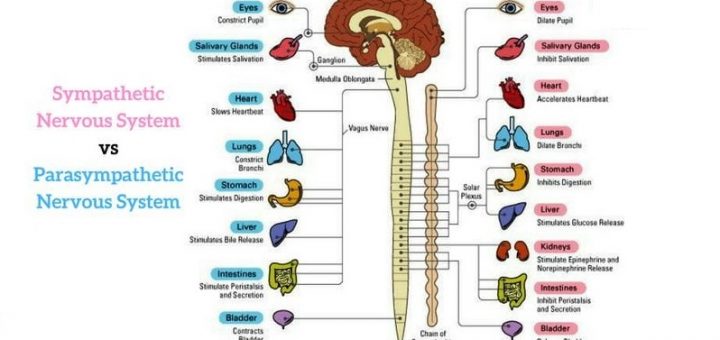
For example sympathetic stimulation on the heart causes an increase in heart rate and force of contraction. Autonomic nervous system ANS involuntary arm of PNS also known as visceral motor division. Most organs have dual innervation.
The autonomic nerves. B the autonomic and somatic nervous branches of the parasympathetic nervous system innervate most organs with opposite functions. Fibers from both division.
Dual innervation of organs by the two branches of the autonomous nervous system functions to a. Set a certain tone of the function of the organs c. Inhibit or stimulate organ function d.
What is meant by dual innervation in the autonomic nervous system. Both branches innervate most organs in an arrangement called dual innervation. Divided into 2 divisions.
They oppose each other. 5 rows DUAL INNERVATION ANATOMY A variety of organs throughout the human body are designed with both. Anatomy of Autonomic Nervous System.
Ensure that the organs can be maximally stimulated when necessary b. Provide stimulatory input and sensory output from the organs e.
One to maintain rest.
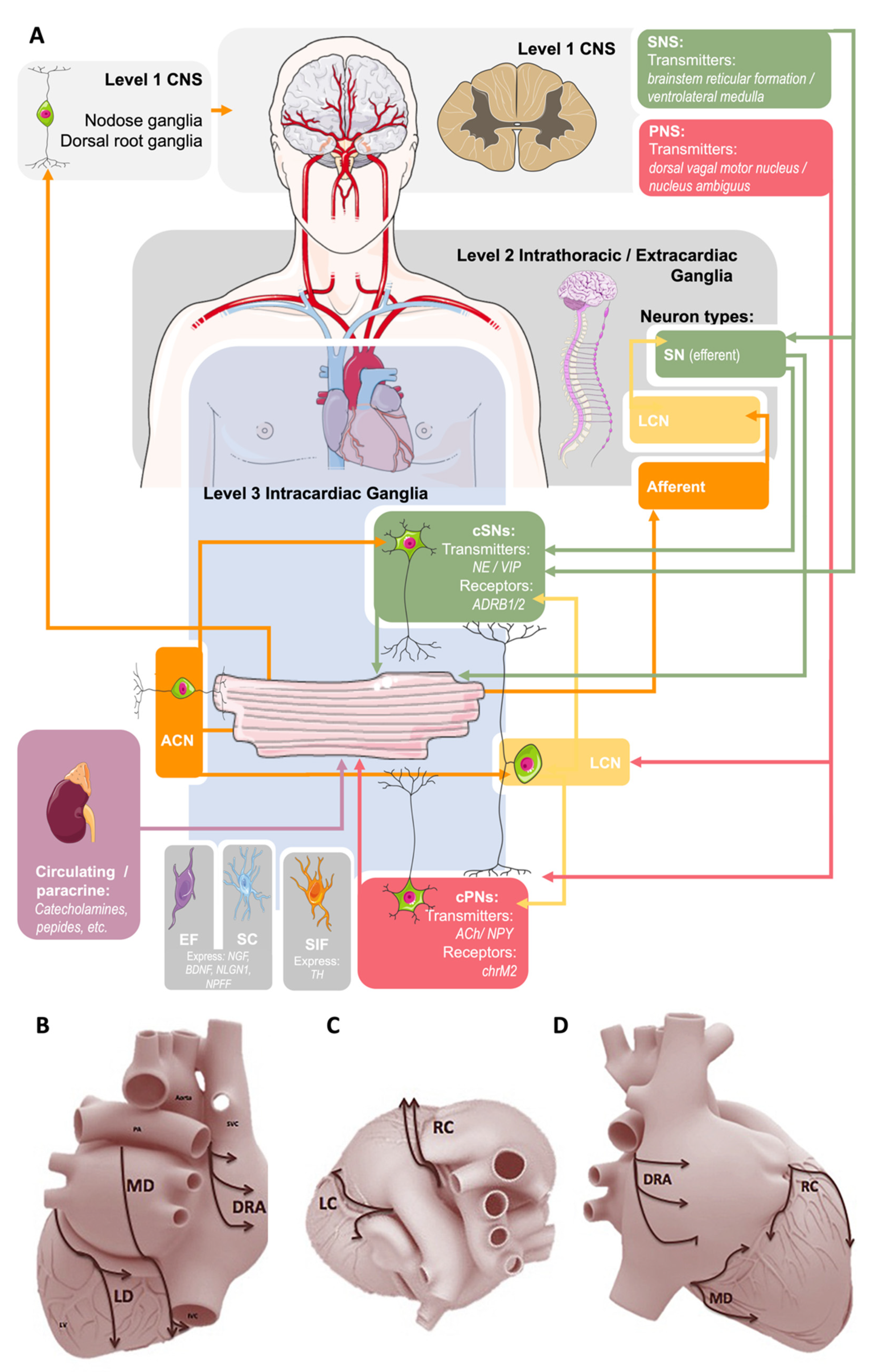
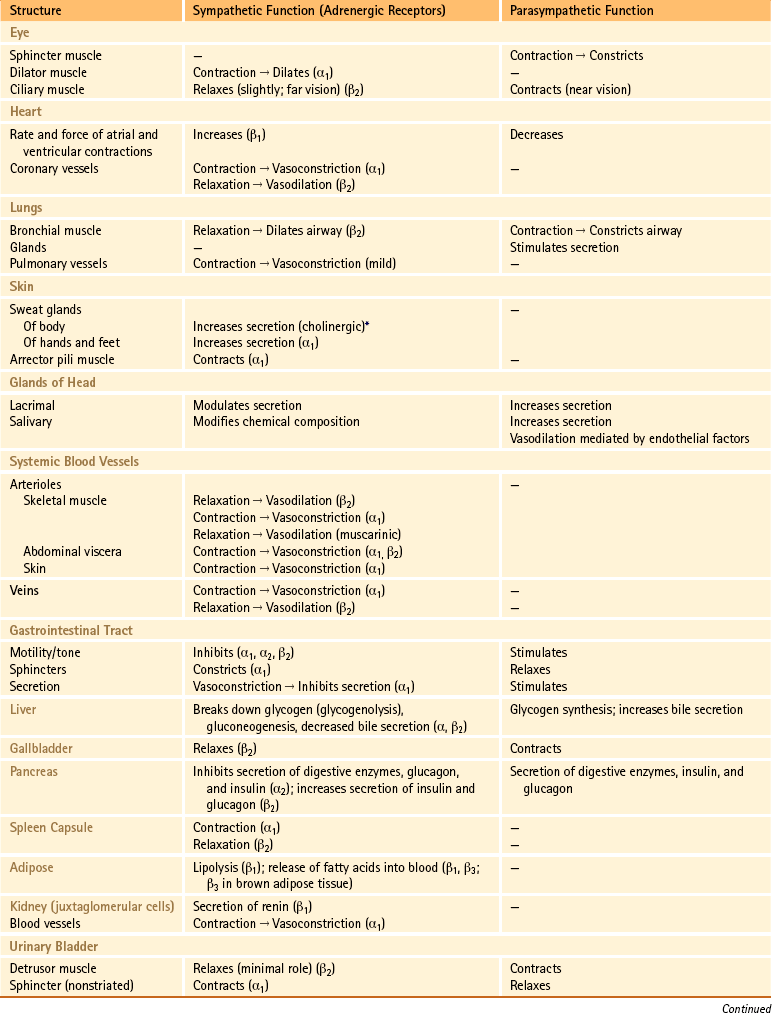
SNS ganglia are found close to the SNS centers in contrast with PSNS ganglia which are farther from the PSNS centers. Dual innervation refers to the innervation of a target organ by both divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic parasympathetic divisions are distinguished by 1. In this condition the effects of the two divisions of the autonomic system may be antagonistic complementary or cooperative table 97. Which branch of the peripheral nervous system is most active during rest. 2 Dual innervation of organs by the autonomic nervous system refers to the observation that A autonomic innervation involves preganglionic and postganglionic neurons. The parasympathetic division is most active during rest and stimulates digestive activities. This means that smooth muscles and involuntary actions such as the heart are regulated by the part of the nervous system that requires no conscious thought but still receives directive from the brain. A ganglion is a neural tissue outside of the CNS which comprises of the neuronal bodies of the second-order neurons whose axons postganglionic fibers provide autonomic innervation to the organs.
This means that smooth muscles and involuntary actions such as the heart are regulated by the part of the nervous system that requires no conscious thought but still receives directive from the brain. Anatomy of Autonomic Nervous System. There are two branches or divisions of the autonomic nervous system ANS. Provide stimulatory input and sensory output from the organs e. The polyvagal theory describes an autonomic nervous system that is influenced by the central nervous system sensitive to afferent influences characterized by an adaptive reactivity dependent on the phylogeny of the neural circuits and interactive with source nuclei in the brainstem regulating the striated muscles of the face and head. Dual innervation of organs by the autonomic nervous system refers to the observation that 2 _____ A both sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons innervate most organs. One to maintain rest and the other to increase activity.












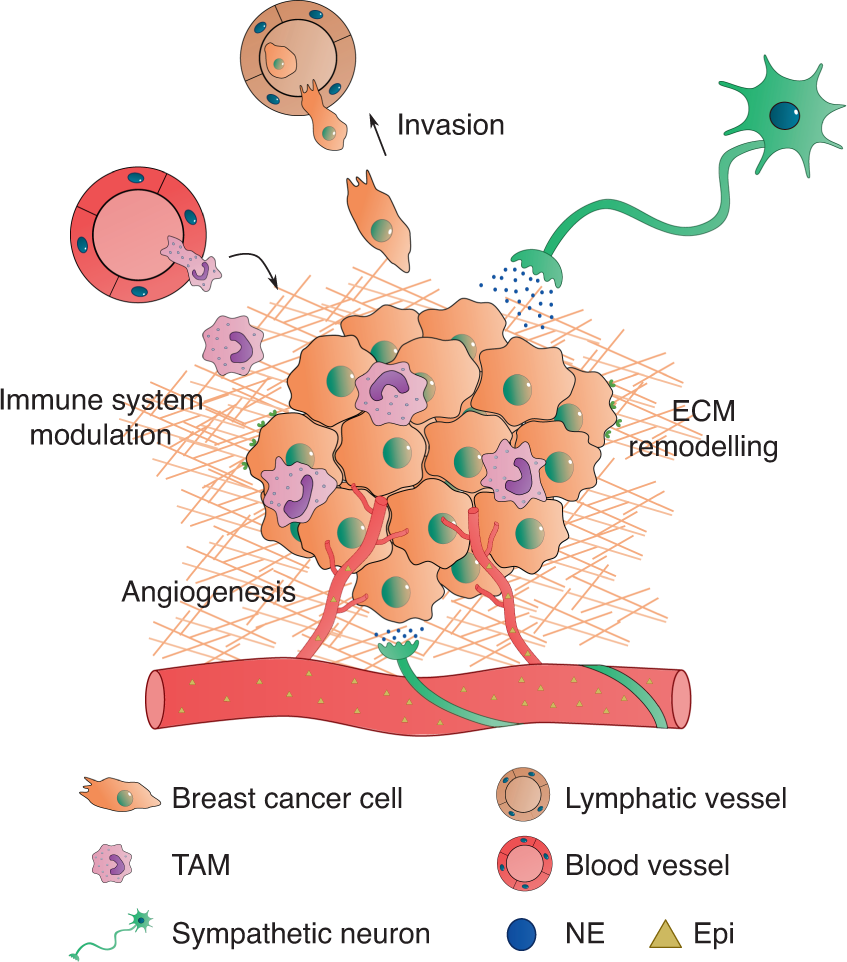
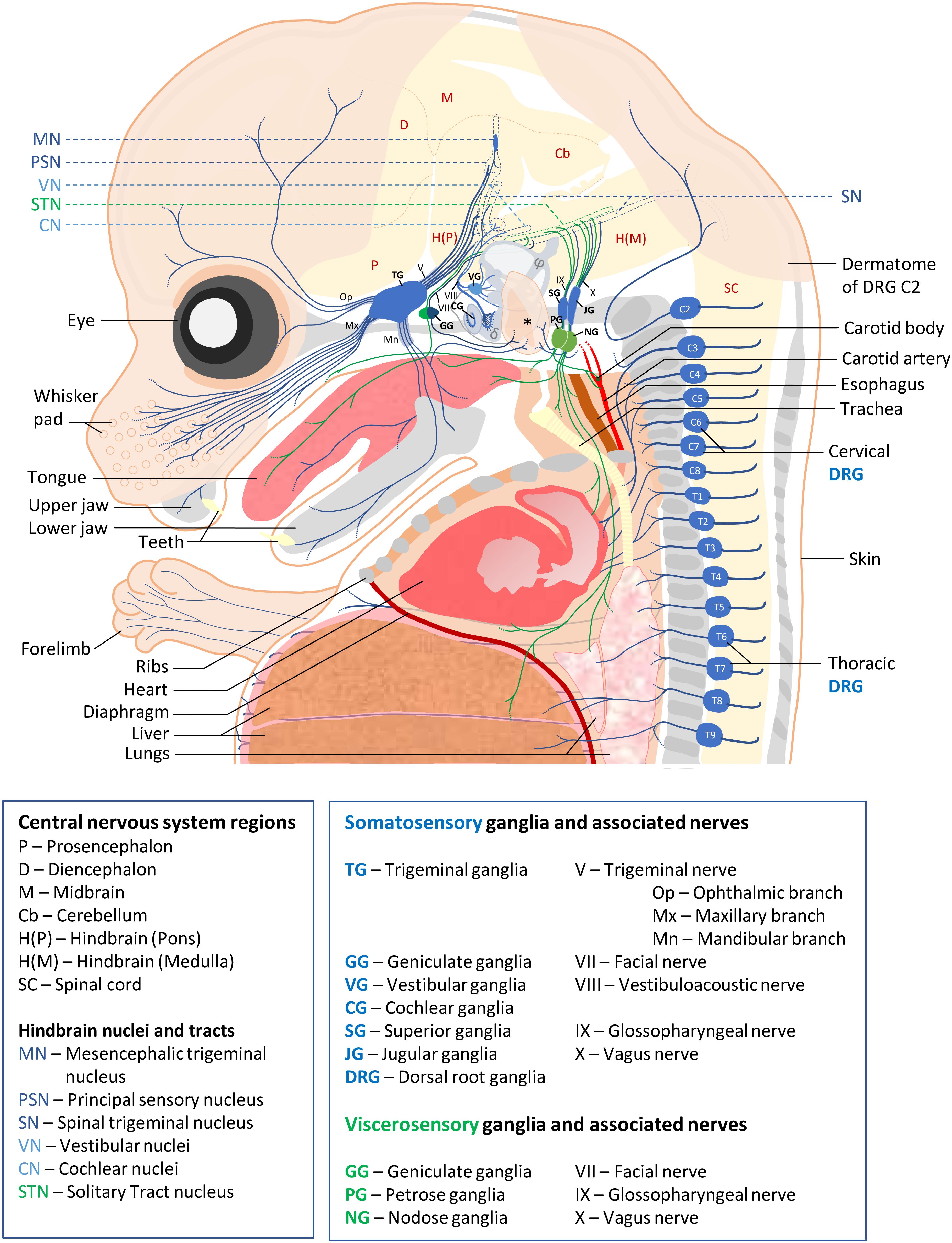
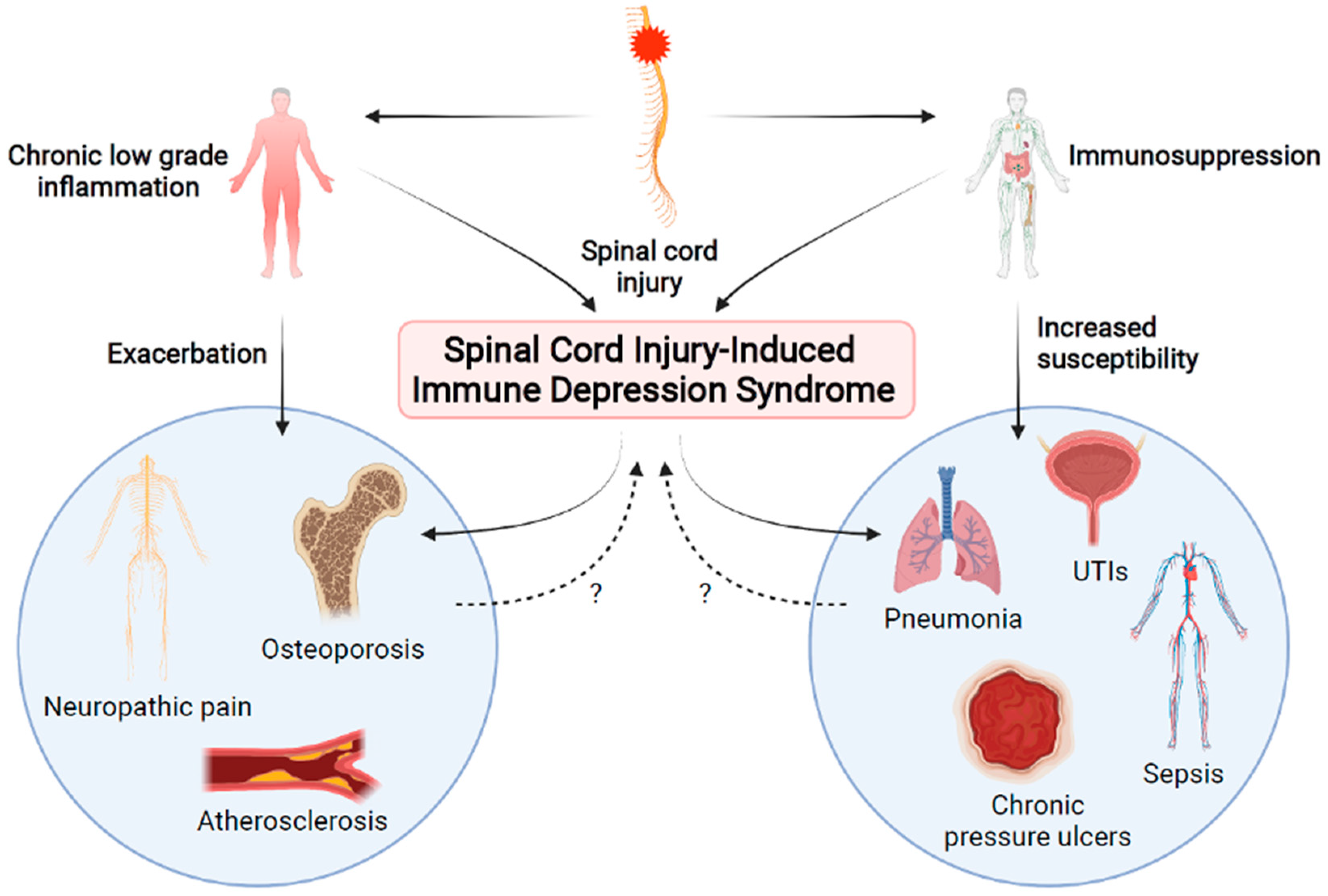
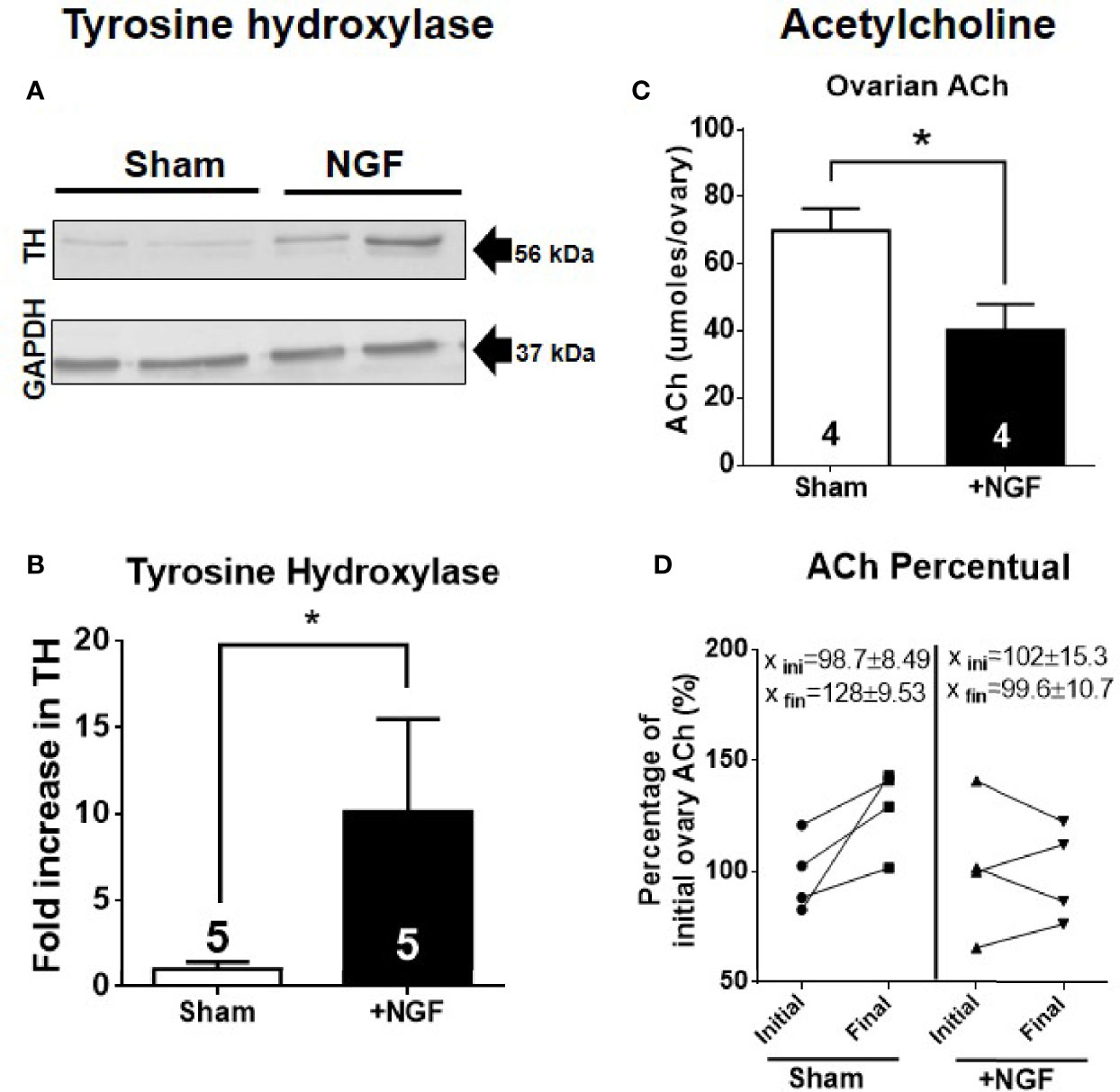

















Post a Comment for "Dual Innervation Of Organs By The Autonomic Nervous System Refers To The Observation That"